Mingyu Kim
k012123600@gmail.com
20-02-2001
Differential-Drive Robot
The differential-drive robot is one of the simplest and most widely used mobile robot architectures, enabling both linear motion and rotation by independently controlling two driving wheels on either side.
By adjusting the relative speeds of the two wheels, the robot can move forward, backward, and even rotate in place.
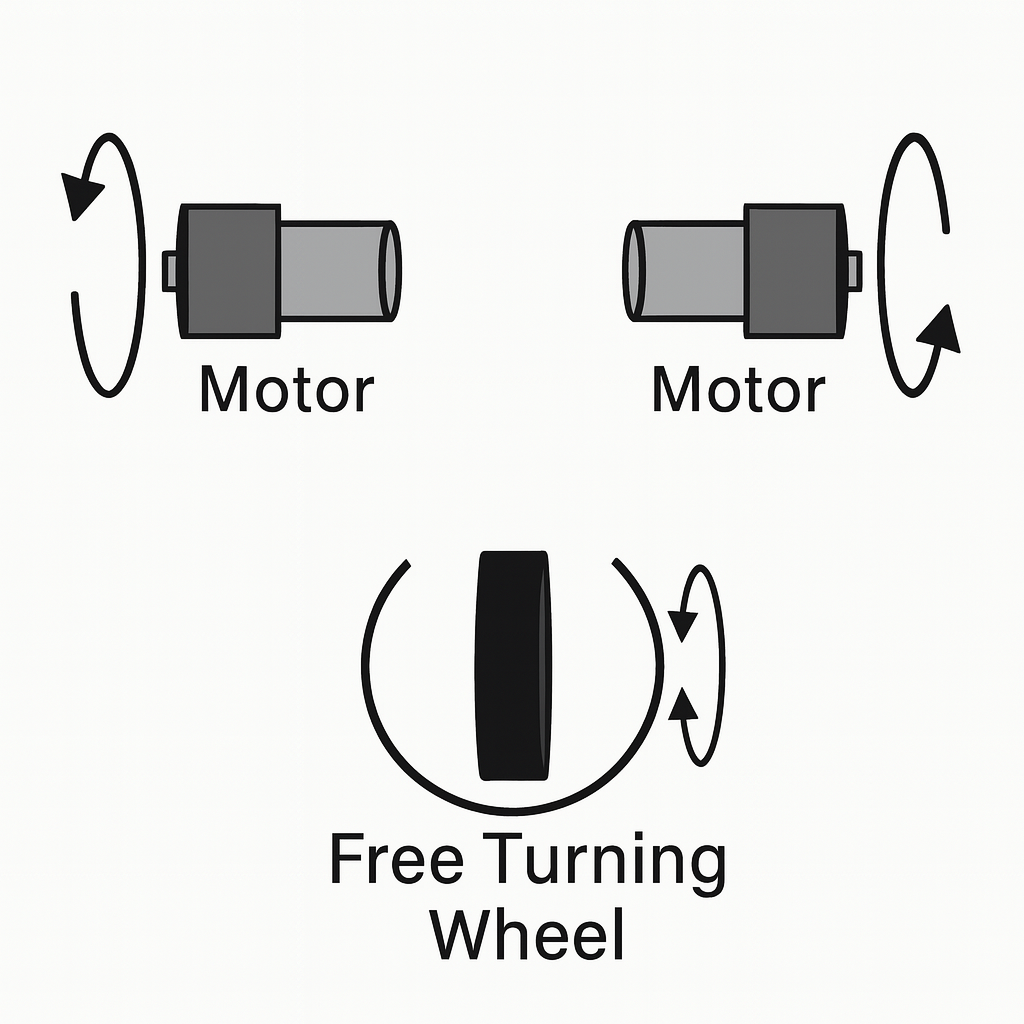
This robot was designed with maximum mechanical simplicity using only two in-wheel motors, and a rear caster wheel was added to ensure posture stability during movement.
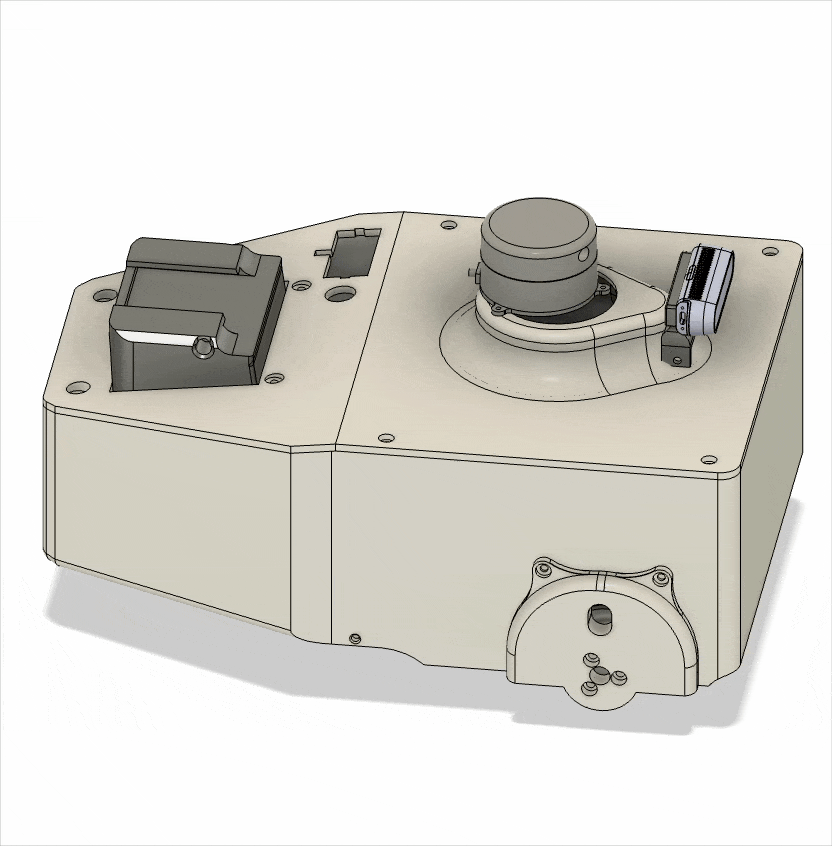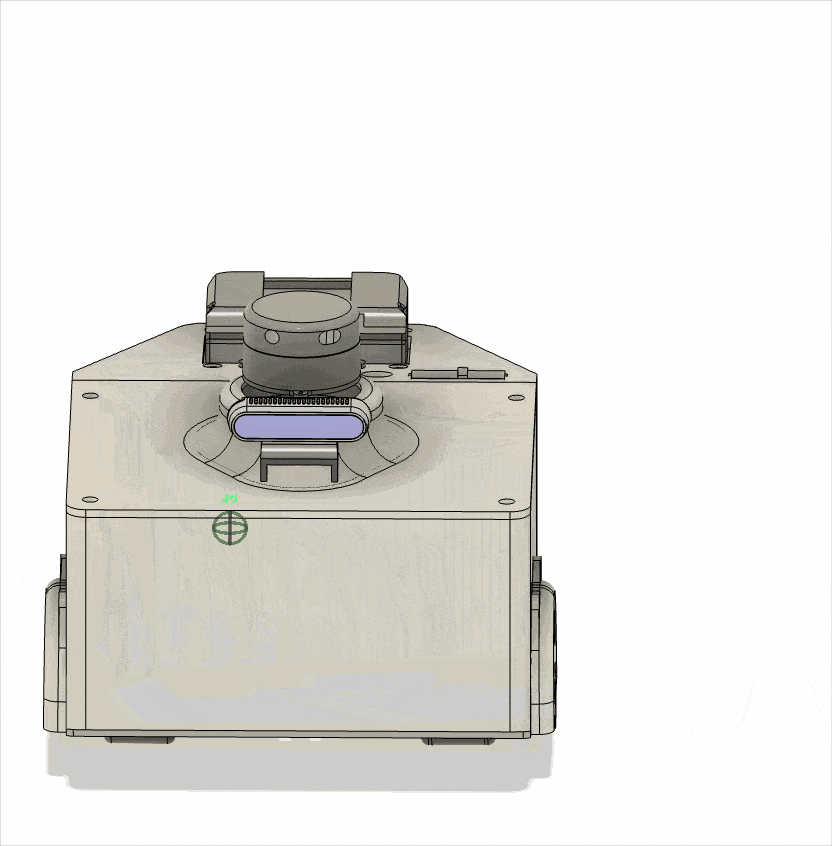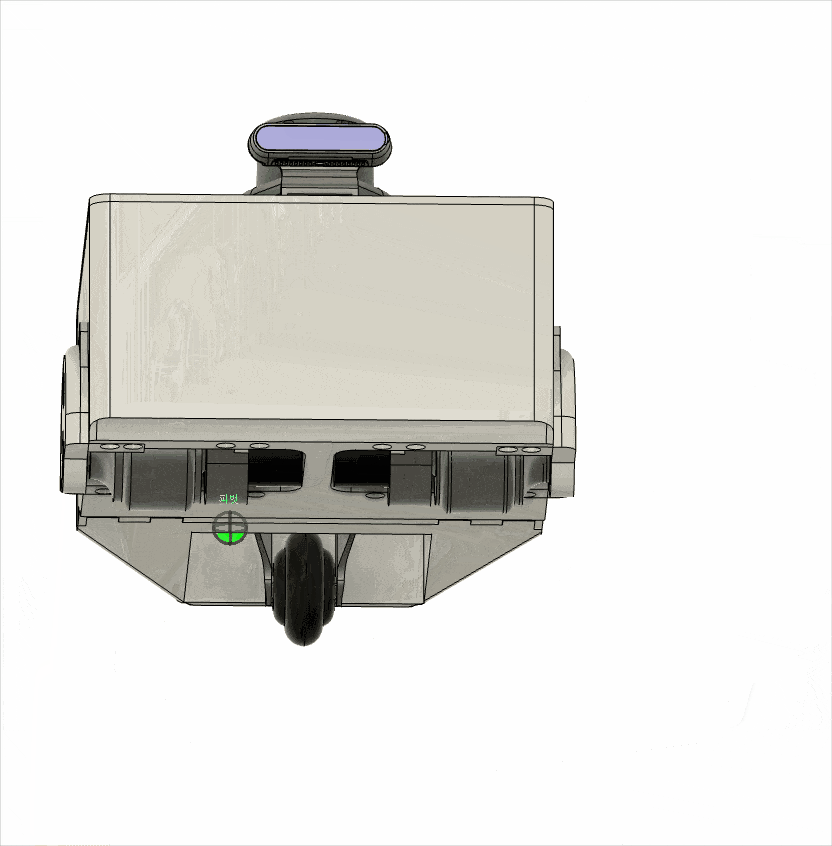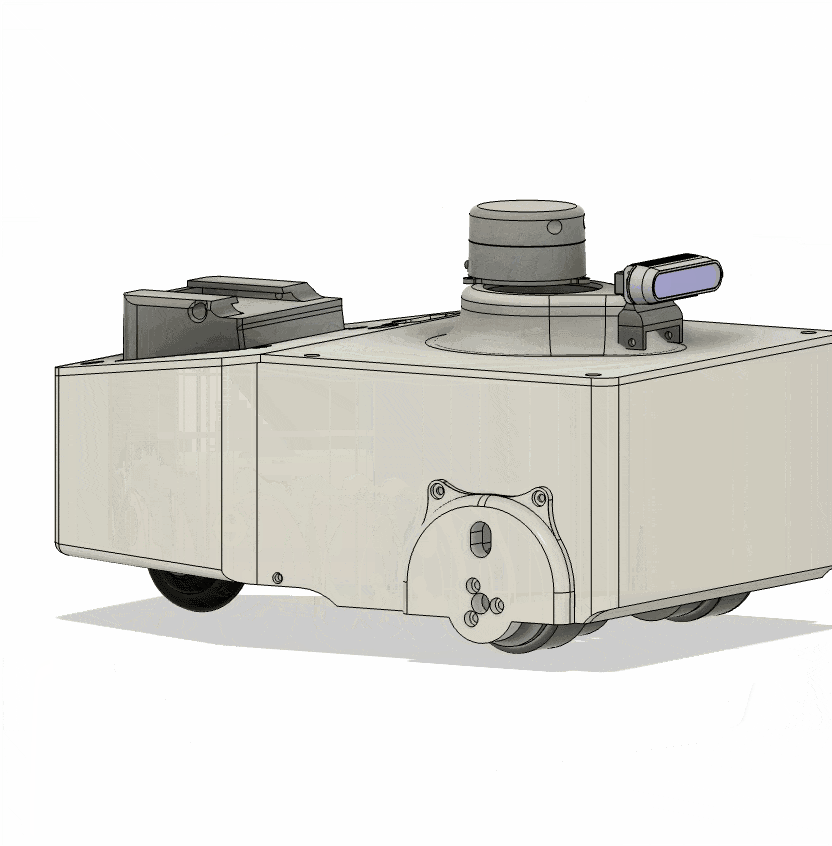
In this project, the differential-drive robot was developed as a compact experimental testbed to broaden the range of robot platforms available for testing the real-world applicability of learning-based path planning methods.

The issue of using non-geared in-wheel motors in this robot has led to reduced stability at low speeds, revealing structural limitations. Therefore, a redesign is currently underway to address this issue.
